Versus Explained: AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
- Datalyst

- Sep 21, 2023
- 1 min read
Updated: Sep 15, 2024

Definitions
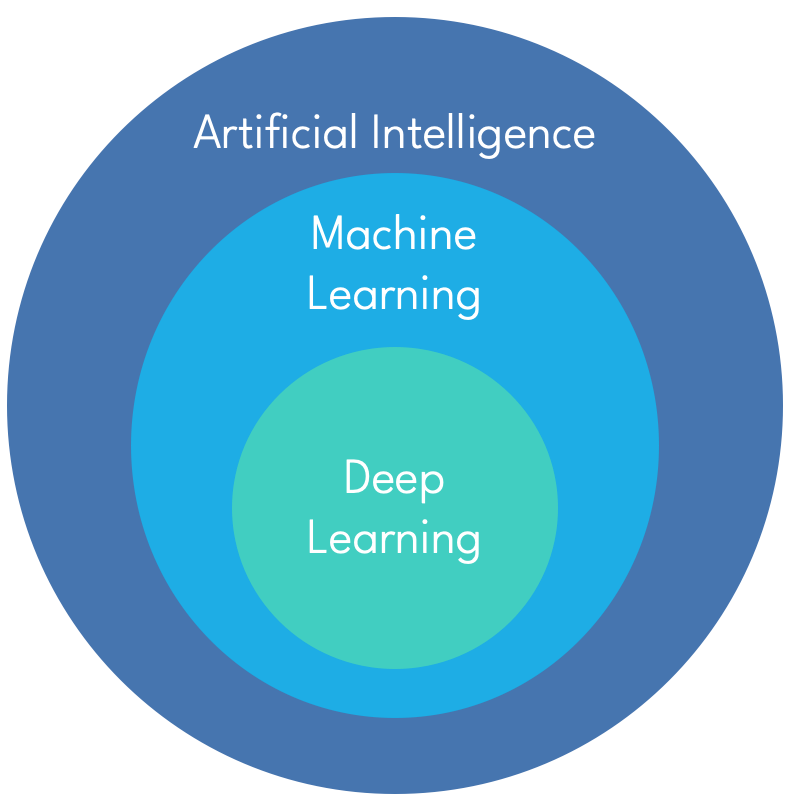
Artificial Intelligence refers to the development of systems or machines that mimic the problem-solving and decision-making capabilities of human intelligence to perform tasks. AI is actually a broad term that covers a full range of systems from "simple" programs like chatbot providing answers based on pre-defined question trees to complex Language Language Models (LLMs) relying on artificial neural networks.
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that uses statical methods and computer algorithms to analyze data and make "intelligent" decisions with minimal user intervention.
One of the key difference of Machine Learning algorithms is their ability to iteratively improve themselves based on the information they collect. Machine Learning relies on different kinds of "models" to Identify and learn patterns from data, which allow them to perform tasks without being explicitly programmed to do so.
Machine Learning models can be divided into three broad categories: supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning (see In depth focus: Machine Learning).
Deep Learning is a specialized subset of machine learning that uses layered artificial neural networks to simulate human decision-making.
Inspired by the human brain, a neural is a collection of small computing units called neurons that take incoming data and learn to make decisions over time.
Deep learning is just referring to the depth of layers of neurons in a neural network (more than 3).

Widely used in the 80s and early 90s, Artificial Neural Networks have known a recent resurgence thanks to the significant increase in computing power.

